Motor Control Centre (MCC)
This guide explains the role of motor control centers (MCCs) in a power distribution system and it explains the need for circuit protection. You will learn how to identify various components of a MCC and the difference between the various classifications and types of motor control center wiring.

Basic Motor Control
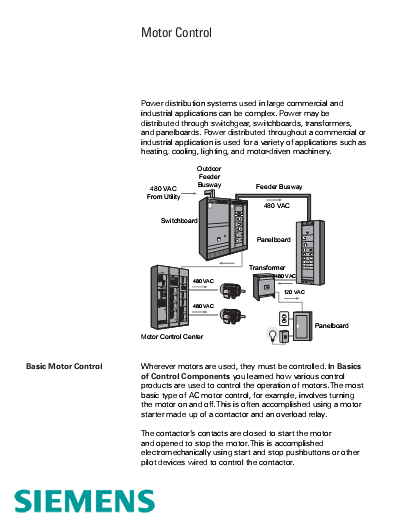
Wherever motors are used, they must be controlled. In Basics of Control Components you learned how various control products are used to control the operation of motors. The most basic type of AC motor control, for example, involves turning the motor on and off.
This is often accomplished using a motor starter made up of a contactor and an overload relay.
The contactor’s contacts are closed to start the motor and opened to stop the motor. This is accomplished electromechanically using start and stop pushbuttons or other pilot devices wired to control the contactor.
Figure 1 – Power distribution and Motor Control Centre connections

The overload relay protects the motor by disconnecting power to the motor when an overload condition exists. Although the overload relay provides protection from overloads, it does not provide short-circuit protection for the wiring supplying power to the motor.
For this reason, a circuit breaker or fuses are also used.
Typically one motor starter controls one motor. When only a few geographically dispersed AC motors are used, the circuit protection and control components may be located in a panel near the motor.
Figure 2 – Basic motor control schematics

Motor Control Centers (MCC)
Numerous commercial and industrial applications necessitate multiple electric motors, and it is frequently advantageous to manage some or all of these motors from a centralized location. The device built for this purpose is the motor control center (MCC).
Additional devices related to the motor, such pushbuttons and indication lights, may also be incorporated.
Figure 3 – Typical motor control panel

Power Supplies used by Motor Control Centers
The primary source of electrical power for motor control centers is an AC generator situated at a power generation facility. AC generators function based on the principle of electromagnetic induction. This indicates that as conductors traverse a magnetic field, a voltage is induced within the conductors. A fundamental generator comprises a magnetic field, an armature, slip rings, brushes, and a resistive load.
An armature consists of many conductive wires (conductors) arranged in loops that rotate within a magnetic field. Only one loop is depicted for clarity.
Figure 4 – When conductors are moved through a magnetic field, a voltage is induced into the conductors

Tracking the rotation of the AC generator over a full 360° round reveals that voltage rises throughout the first quarter, peaking at a maximum positive value at 90°. The voltage will diminish throughout the second quarter of the revolution, until reaching zero at 180°. In the third quarter of a revolution, voltage would rise in the opposite direction until it attained a maximum negative value at 270°.
In the final quarter of a revolution, the voltage would diminish until it hit zero at 360°. This constitutes a full cycle or a complete alternation between positive and negative.
Figure 5 – Voltage cycles

The armature of the simple two-pole AC generator depicted above revolves at 3600 revolutions per minute (RPM), resulting in the generation of 60 cycles of voltage every second, equivalent to 60 hertz (Hz).
Should the generator had four poles, it would produce the requisite 60 Hz at a rotational speed of 1800 RPM.
Three-Phase Voltage
Three-phase power is utilized in the majority of extensive commercial and industrial motor applications. In a three-phase system, the generator generates three voltages. Each voltage phase oscillates at the same frequency (60 Hz in the U.S. and 50 Hz in several other nations).
The phases are displaced by 120° relative to one another.
Figure 6 – Three-phase power

Motor control centers receive electricity via intricate distribution networks comprising power distribution wiring and associated devices. Transformers operating with three-phase electricity necessitate three interlinked coils in both the primary and secondary windings. These transformers can be configured in either a wye or delta arrangement.
The transformer type and real voltage are contingent upon the specifications and capacity of the power company, as well as the customer’s requirements. The subsequent figure depicts examples of the secondary windings of wye and delta transformers.
Note that these are merely examples, and alternative transformer secondary voltages may exist.
Figure 7 – Examples of the secondary windings of wye and delta transformers

Motor Rotation
Three-phase voltage is utilized in extensive commercial and industrial establishments to operate AC motors. An AC motor consists of a stationary component, known as the stator, and a rotating component, referred to as the rotor.
Three-phase alternating current is supplied to the stator via the power connections.
Figure 8 – Three-phase motor

The rotational direction of a three-phase AC motor rotor is determined by the phase sequence of the supplied power. In this example, L1 (A) is linked to motor lead T1, L2 (B) is linked to motor lead T2, and L3 (C) is linked to motor lead T3.
When electricity is supplied via the “F” connections, the motor rotates in a clockwise (forward) direction.
| Title: | Basics of Motor Control Centers – SIEMENS |
| Format: | |
| Size: | 4.3 MB |
| Pages: | 72 |
| Download: | Right here | Video Courses | Membership | Download Updates |


I want to share the latest technology trend of the motor control center
I am interested in your services
Do we require the use of energy meter per MCC?
Can i place MCC inside Low voltage Switch Room together with other Switchboards
Of course you can.
What is minimum spaces in between office table and MCC 600V?
dear sir,
at motor control unit have 1 regulator switch for connecting power supply what’s have name
Looking for information on MCC.
i want to set up MCC Panel with 10 motors and panelboard for lightings and power outlet.
Are there any set standards for numbering breakers in an MCC?
Hi can you please forward me the 4.3mb Basics of motor control centers because
I need to set up panels for MCC. for 12 electric motors
thanks for sharing useful information
please can you forward me the 4.3 MB Basics of Motor Control Centers
What is the maximum ambient operating environment recommended for a MCC?
Very useful article. Thanks a lot.
What I understood is that the only purpose of the MCC is to group all the motor starters together in one place to reduce the cost of using multiple cables for each motor starter and that, in the MCC, each box has the starter and protection devices for the motor.
This is a very useful article to understand the basics of MCC. Thanks for uploading
Hi kindly can I have the link to download this article and thanks
HEY M WORDERING MAYBE YOU MIGHT HELP, M LOOKING FOR ELECTRIC MOTOR CONTROL CENTRE OR SUPPLIER
Hola cómo están. Muy buena la información, me gustaría que los PDF se pudieran descargar en español.
This article is excellent. Thank you Evan!
Tanks for the article. It’s a good one. However please I need you to send to me a student project on the design and construction of a 2KVA inverter with a pure sinewave output.
it is very useful for me
thanks
Thanks for your great work.
Hello, can you guys give us a aproximate cost for a motor control center for a water pumping station?
Thank you,
Hi. Could you please send me the 4.3MB Basics of motor control centres.
hi, just wondering, for panel schamtic design. should the layout of the schamtic be power section, control wiring section and then a BMS section. or should power supplies and control wiring be shown on the same page ?
Thank you , its really helpfull
please can you forward me the 4.3 MB Basics of Motor Control Centers
Hi Can you please forward me the 4.3 MB Basics of Motor Control Centers ,because I am been blocked from our administrator.
Thank you